Configuring your compiler
Picking a Compiler
Depending on what platform(s) you want to target for your Minecraft: Bedrock Edition mod, you'll have to use the correct compiler and standard template library (STL) for complete ABI compatibility for both language features and library features.
The following table serves as a rough guide for which compiler you'll want to use for a given Bedrock platform. It's not exact, nor complete (for now):
| Platform | Compiler | STL |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | MSVC | Microsoft STL |
| Android | GCC | libstdc++ |
| OSX/iOS | Clang | libc++ |
Generally, it should be fine to use the latest releases of both the compiler and STL provided by the table. If any notable incompatibilities are found in the future, the table will be updated accordingly.
IMPORTANT
If you are targeting Windows, the correct runtime library must be configured, continue reading.
Setting the Runtime Library
When targeting Windows, STL container ABI and C Runtime function compatibility are affected by the runtime library being used (either Release or Debug). Since official Minecraft: Bedrock Edition releases are compiled with the Release mode libraries, your mod must use the Release mode libraries, even when compiling a debug build.
CMake
CMake 3.15 introduced the MSVC_RUNTIME_LIBRARY property. There are 2 relevant values:
MultiThreaded- Statically linked, release mode runtime libraryMultiThreadedDLL- Dynamically linked, release mode runtime library
Opting for the dynamically linked runtime library will require users of your mod to have the associated Visual C++ Redistributable downloaded, in exchange for a smaller binary size. The inverse is true of the statically linked runtime library.
It is often faster to compile against the dynamically linked runtime library, so it's worth considering dynamic linkage for debug builds and static linkage for release builds. A CMake generator expression can facilitate this behavior:
set_property(TARGET MyTarget PROPERTY
# Statically link in release mode and dynamically link in debug mode
MSVC_RUNTIME_LIBRARY "MultiThreaded$<$<CONFIG:Debug>:DLL>")Or if you only want to use one runtime library for all build types:
set_property(TARGET MyTarget PROPERTY
MSVC_RUNTIME_LIBRARY "MultiThreaded")set_property(TARGET MyTarget PROPERTY
MSVC_RUNTIME_LIBRARY "MultiThreadedDLL")Clang on Windows
IMPORTANT
Some modding platforms, such as Amethyst, do not support Clang.
The Clang compiler supports ABI compatibility with MSVC. While it is not fully compatible, it is in a state that is acceptable for most applications, including developing mods for Minecraft: Bedrock Edition.
This is best done through the clang-cl.exe driver program, which is a "drop-in" replacement for MSVC's cl.exe.
Incompatibilities
A common issue that is encountered when using Clang instead of MSVC is the incompatibility with entt::type_hash. To address this issue, see Type Hashes.
Downloading LLVM
Open the Visual Studio Installer and select "Modify" on your installation.
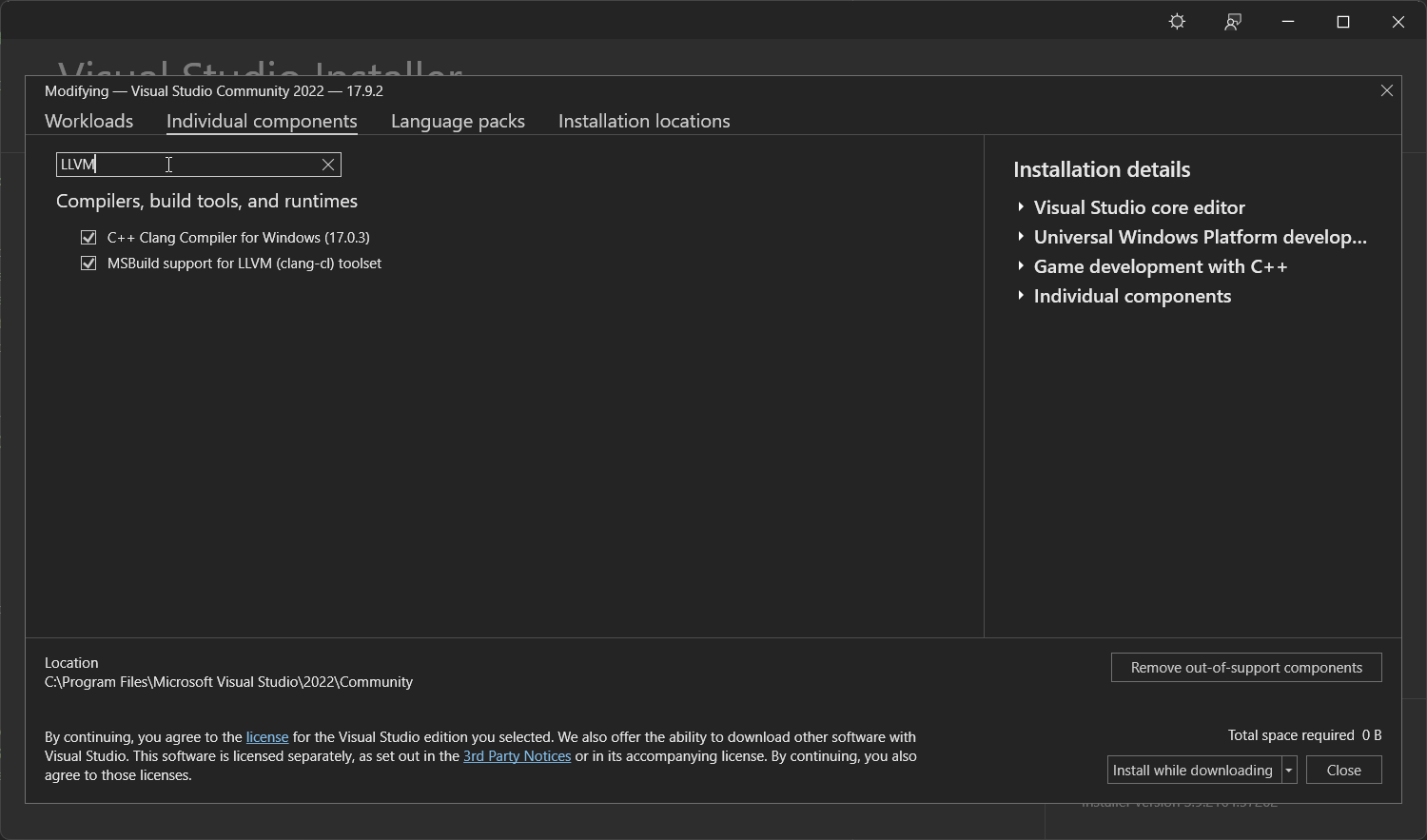
Click on "Individual Components" at the top and search for "LLVM". Make sure that both "C++ Clang Compiler for Windows" and "MSBuild support for LLVM" are selected.
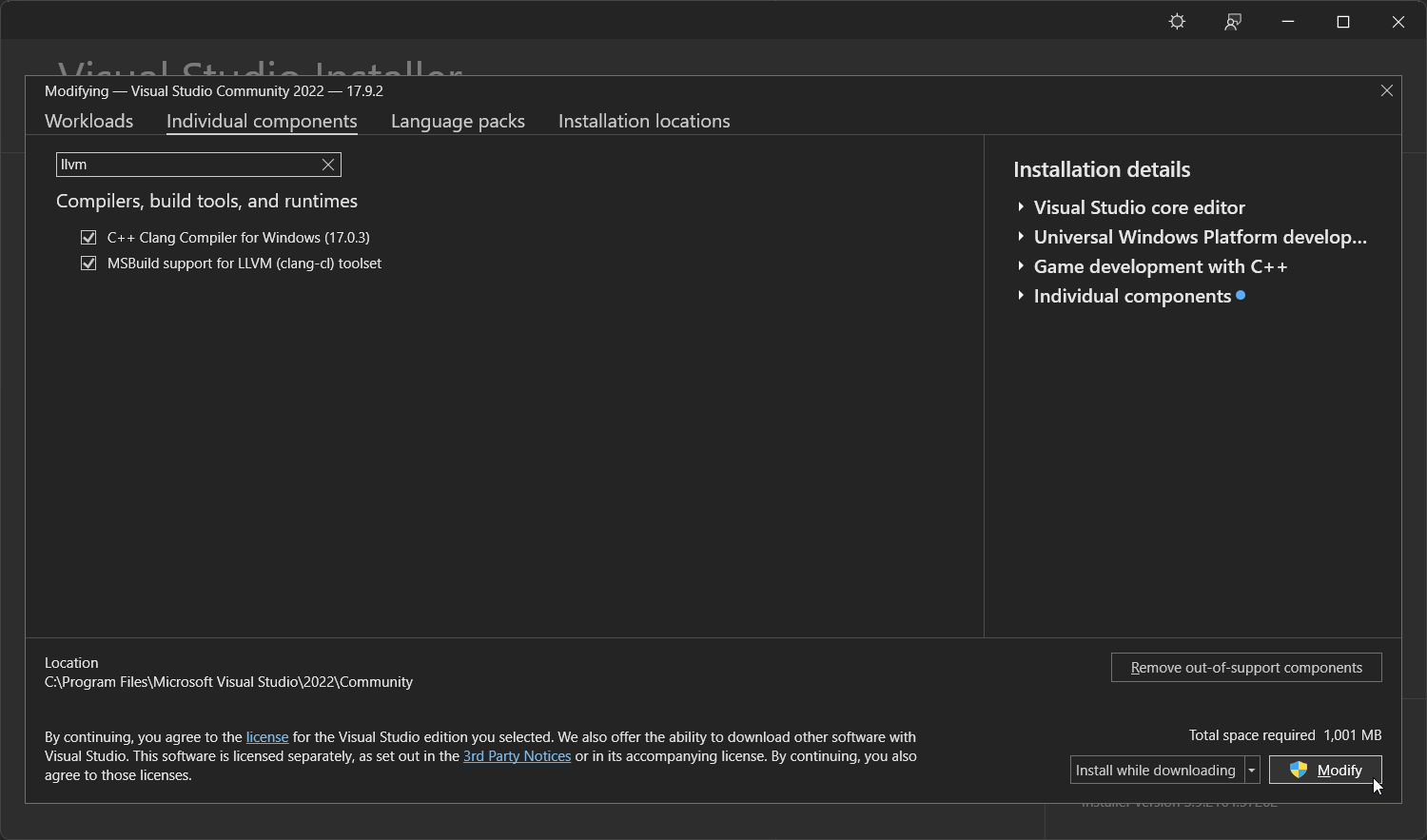
Click "Modify" in the bottom right and wait for the installation to complete.
Visual Studio + MSBuild
Open Microsoft Visual Studio and navigate to Project > [Your Project Name] Properties
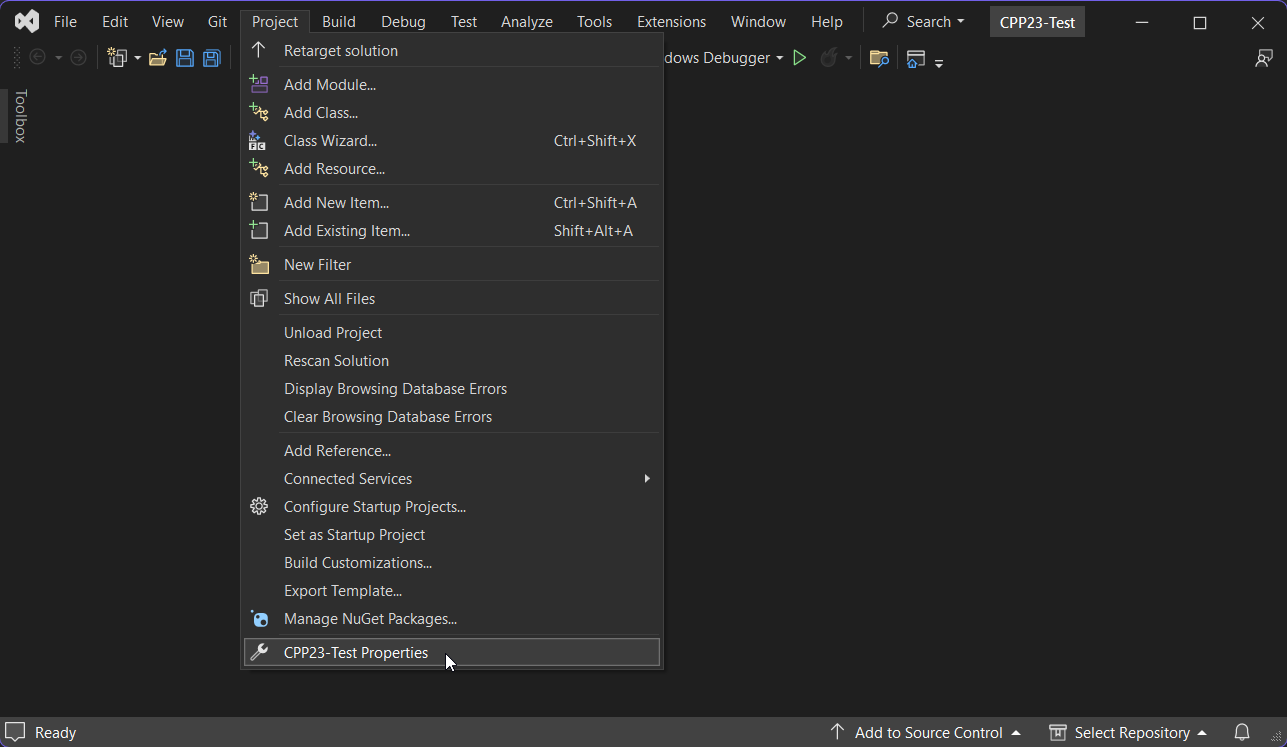
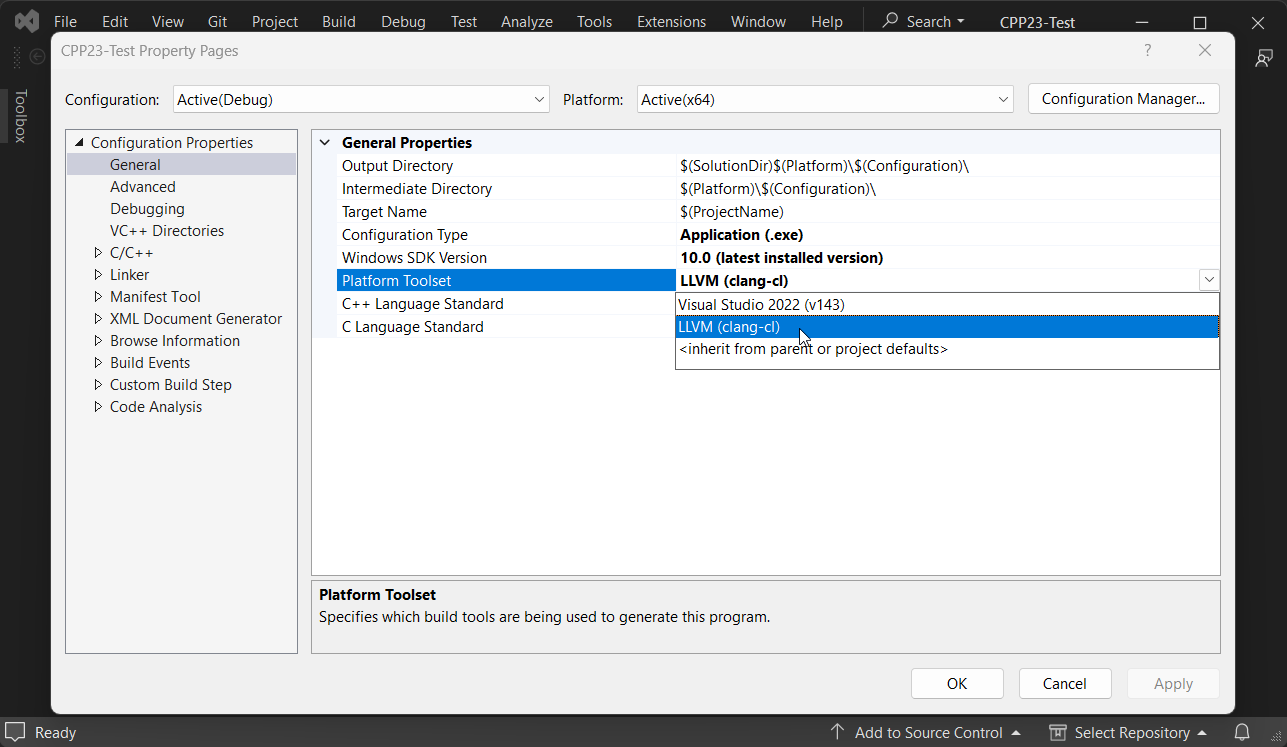
Select "LLVM (clang-cl)" from the "Platform Toolset" dropdown.
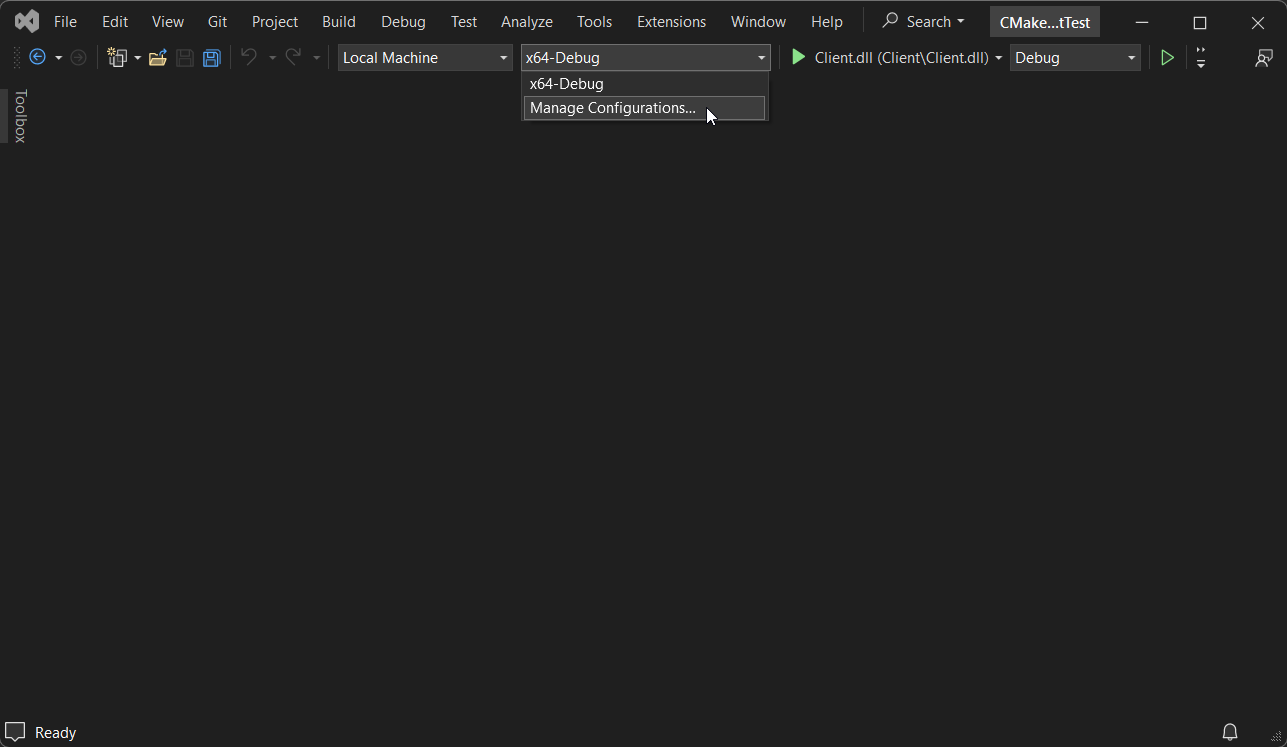
Visual Studio + CMake
Click on "Manage Configurations" under the build type dropdown.
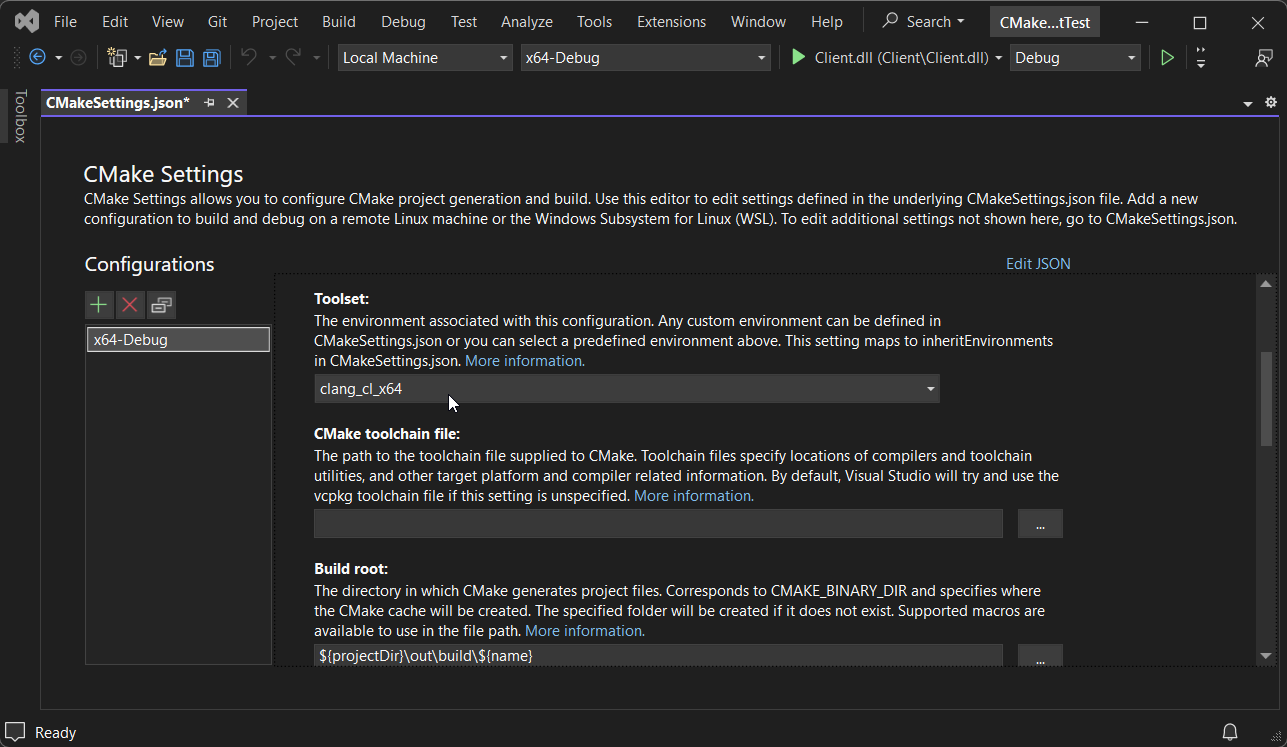
Select clang_cl_x64 for the desired build configurations.
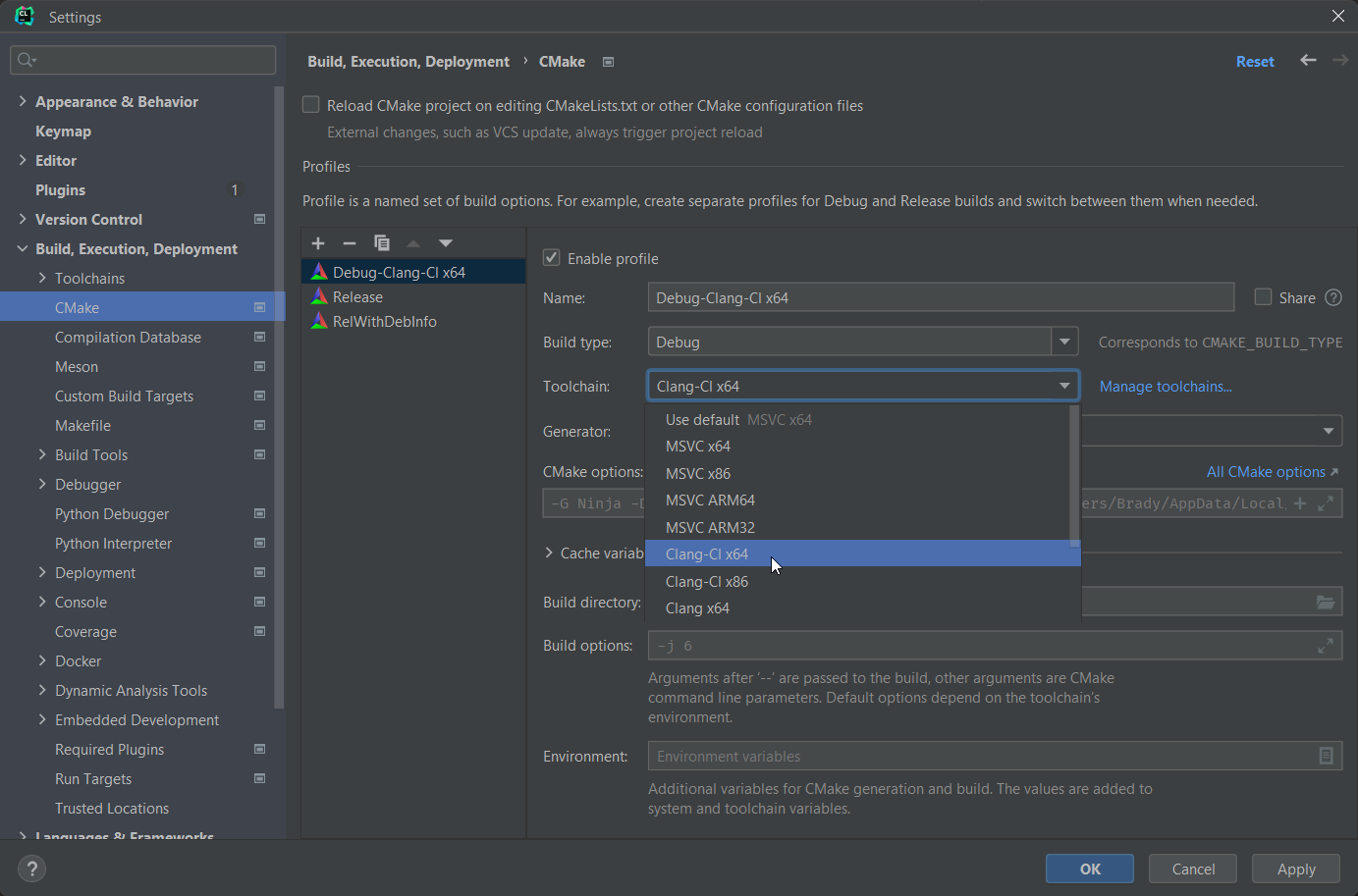
CLion
Open the IDE settings through File > Settings or using Ctrl+Alt+S.
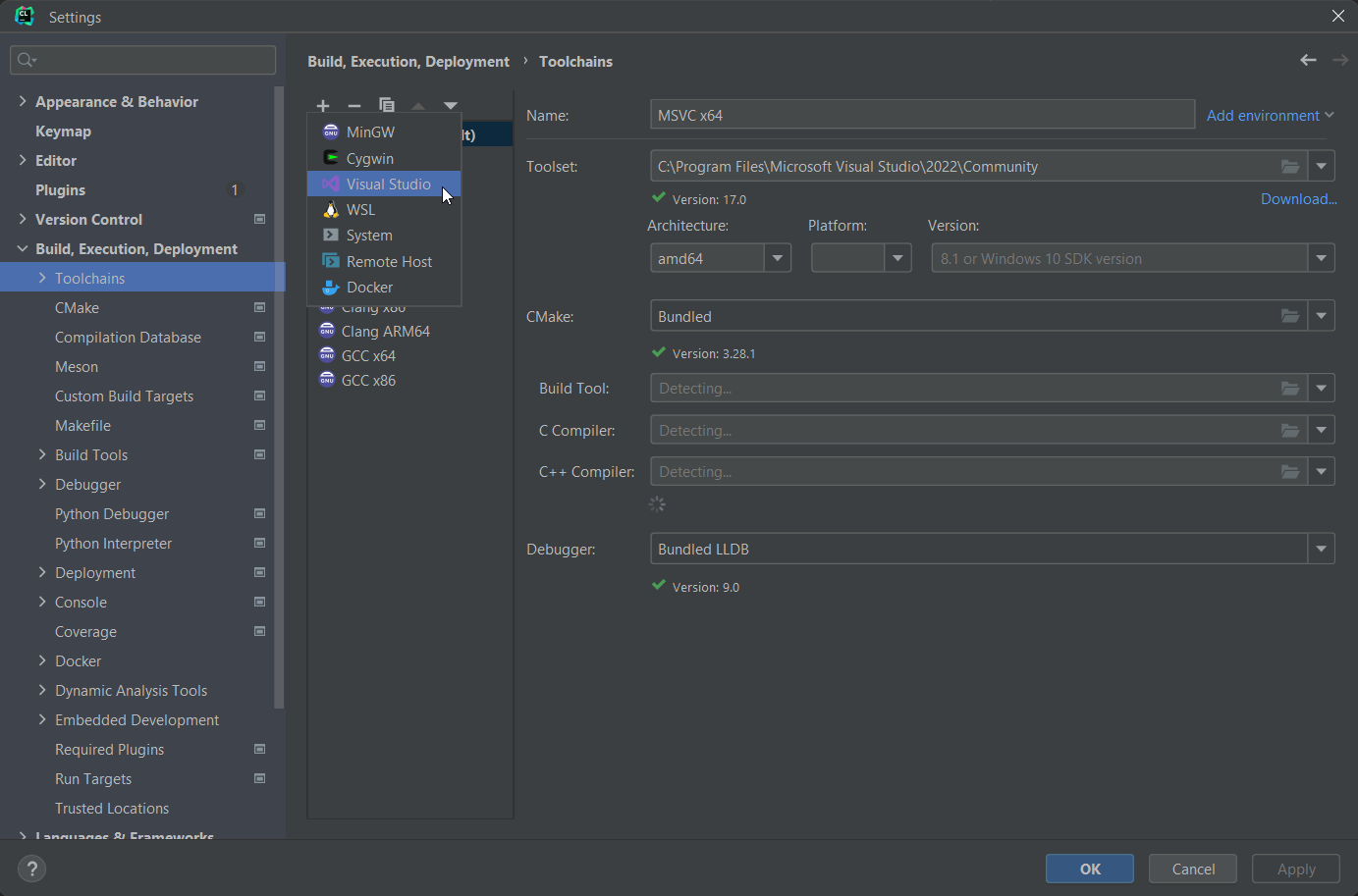
Navigate to Build, Execution, Deployment > Toolchains and add a new "Visual Studio" toolchain.
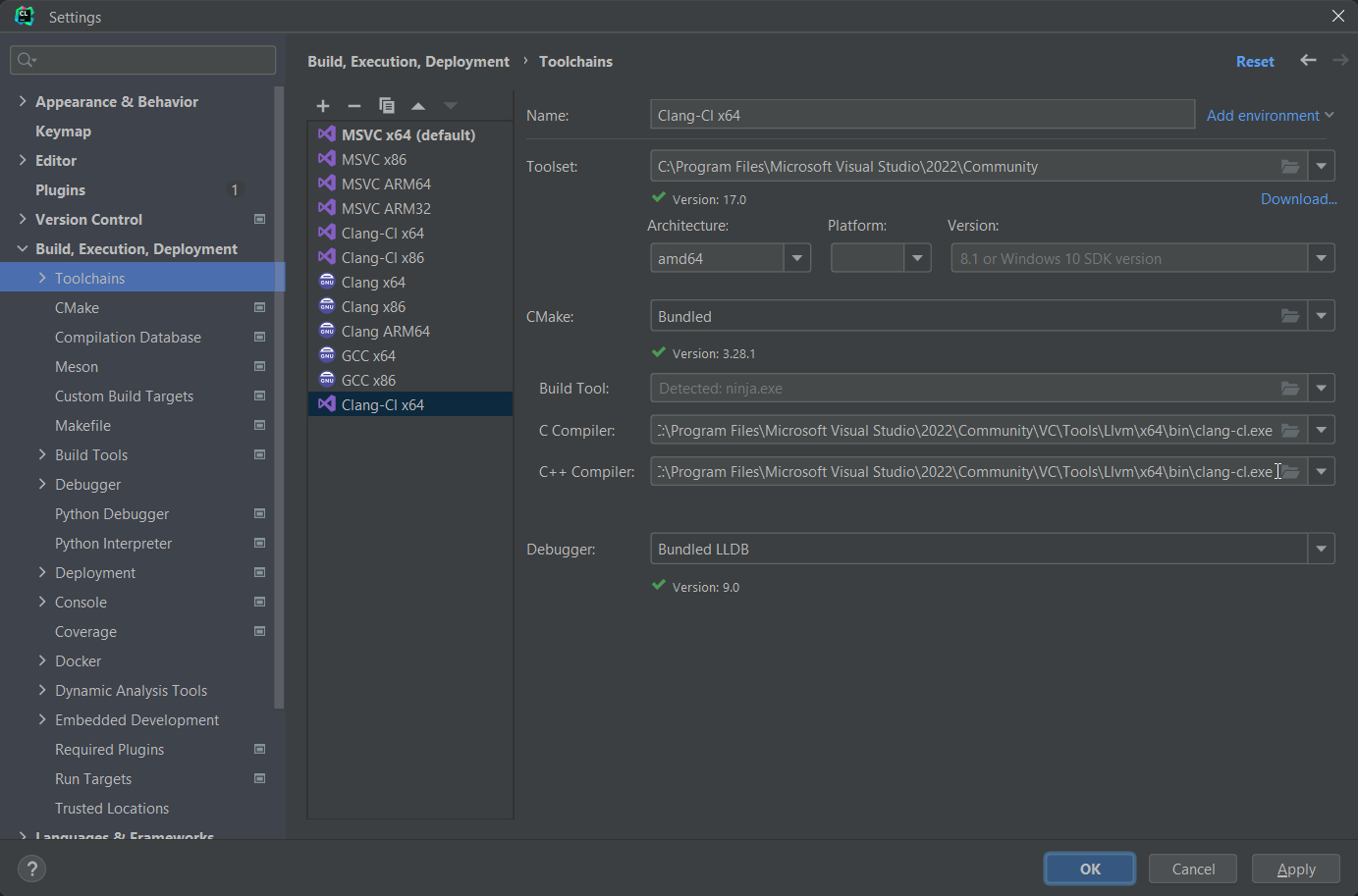
Set the "Architecture" field to amd64 and the C and C++ compiler paths to [VS Install Dir]\VC\Tools\Llvm\x64\bin\clang-cl.exe.
Navigate to Build, Execution, Deployment > CMake and set the toolchain in the relevant CMake profiles to the Clang-Cl toolchain we just created.